Perched atop countless homes, roof vents are often overlooked yet play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy living environment. These unassuming fixtures dot our rooflines, silently working to regulate the conditions within our attics and, by extension, our entire homes.
As homeowners, we may rarely give them a second thought, but understanding their purpose can shed light on their importance in preserving the integrity of our dwellings.
From scorching summer heat to frigid winter chills, our homes face a barrage of environmental challenges throughout the year. Amidst these fluctuations, roof vents stand as silent sentinels, performing a vital function that impacts everything from energy efficiency to structural longevity.
Whether you’re a curious new homeowner or a seasoned DIY enthusiast, understanding roof ventilation can provide valuable insights into your home’s performance. In this exploration, we’ll uncover the multifaceted purposes of these often misunderstood components and why they deserve our attention.
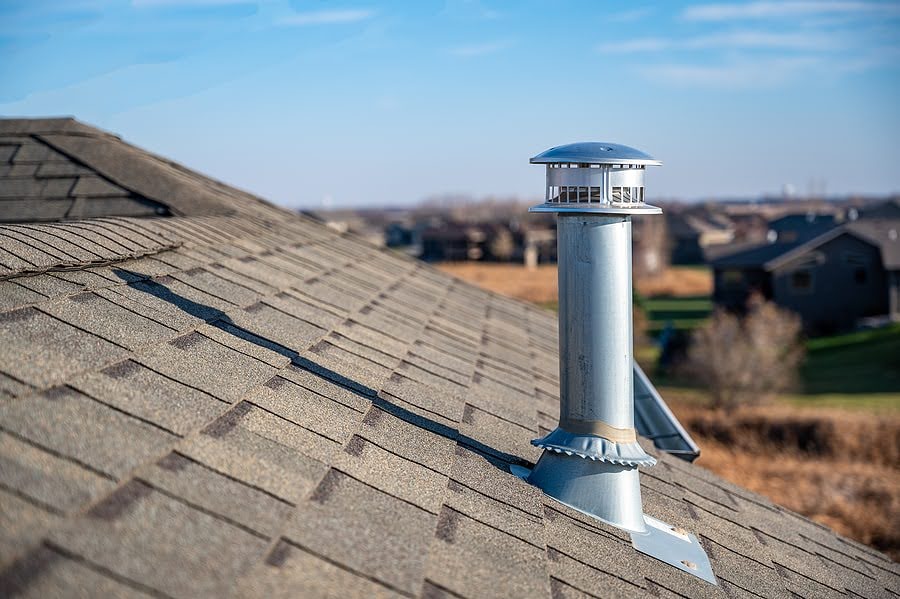

What Are Roof Vents For?
Roof vents are crucial components of a well-designed roofing system, playing a vital role in maintaining proper airflow and ventilation within the attic space of a building. They help regulate temperature and moisture levels, contributing to the overall health of your home’s structure.
These essential elements create a balanced environment in your attic, which in turn affects the comfort of your living spaces below. By facilitating air movement, roof vents help prevent a host of potential issues that can arise from stagnant, humid air.
Proper roof ventilation is often overlooked in home maintenance, but its importance cannot be overstated. From preserving the integrity of your roofing materials to improving energy efficiency, roof vents are key to maintaining a healthy, comfortable, and structurally sound home.
How Do Roof Vents Work
Roof vents operate on a simple yet effective principle of air circulation. They create a pathway for hot air to escape from the attic while simultaneously drawing in cooler air from outside. This continuous exchange helps maintain a balanced temperature and humidity level in the attic space.
The process works through natural convection, where hot air rises and exits through upper vents (such as ridge vents), creating negative pressure that pulls in cooler air through lower vents (like soffit vents). This creates a constant flow of air, preventing stagnation and buildup of heat and moisture.
This ventilation system works year-round, adapting to changing seasonal conditions. In summer, it helps expel hot air that can make your home uncomfortable and increase cooling costs. In winter, it helps regulate humidity levels, preventing condensation that can lead to moisture damage.
Purpose of Roof Ventilation
The primary purpose of roof ventilation is to regulate attic temperature and moisture levels. In summer, it prevents heat buildup that can make homes uncomfortably warm and increase cooling costs. It also protects roofing materials from excessive heat, preventing premature aging and deterioration.
In winter, roof ventilation reduces attic humidity, preventing condensation issues when warm, moist air meets the cold roof underside. Proper airflow helps prevent moisture buildup, protecting the roof structure and insulation from water damage. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your roofing system year-round.
Beyond temperature and moisture control, roof ventilation maintains consistent roof surface temperatures. This is particularly important in colder climates, where it can prevent ice dams – a common problem occurring when warm attic air causes snow to melt and refreeze at the roof’s edge.
Types of Roof Vents
There are several types of roof vents, each designed for specific ventilation needs. Ridge vents are one of the most common and effective types, running along the peak of the roof to provide continuous airflow. These are often paired with soffit vents, allowing fresh air to enter the attic space from the underside of the roof’s overhang.
Gable vents are another popular option, installed on the exterior wall of the attic at the gable ends of the house. These work well in conjunction with soffit vents to create a cross-flow of air. Turbine vents, also known as whirlybirds, use wind power to create suction that draws hot air out of the attic.
Other types include static vents, which are simple openings on the roof surface, and powered attic ventilators, which use electric fans to forcefully expel hot air. Many homes use a combination of these vent types to achieve optimal ventilation tailored to the specific architecture and climate conditions.
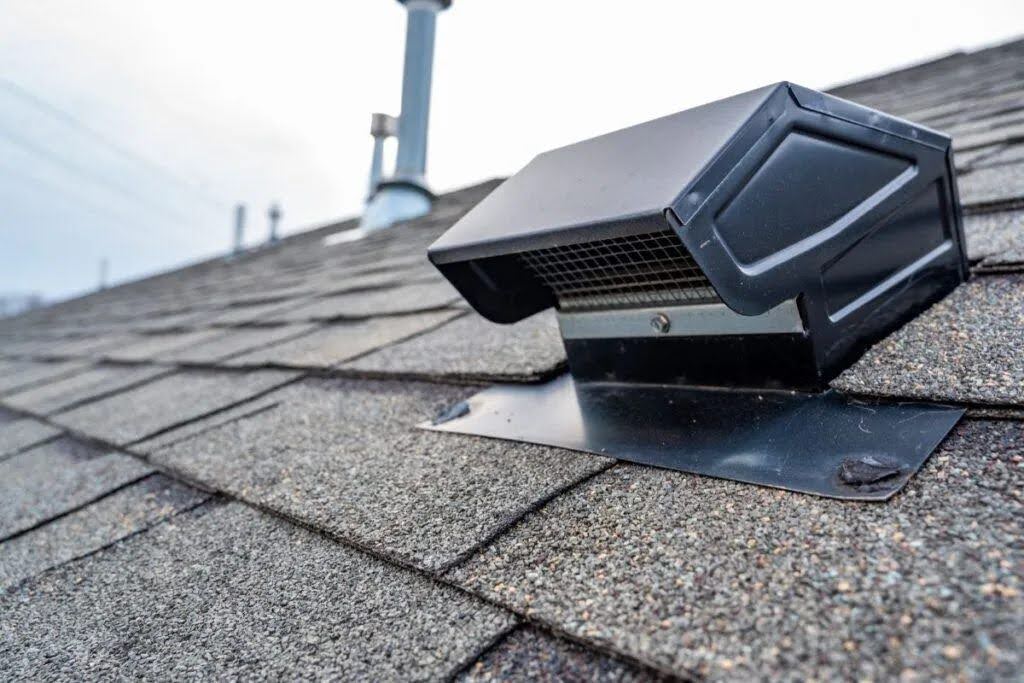

Benefits of Proper Roof Ventilation
Adequate roof ventilation offers numerous benefits to homeowners, starting with extending the lifespan of your roof. By preventing heat and moisture buildup, proper ventilation helps protect shingles and underlying structures from premature aging and damage, potentially saving thousands in early roof replacement costs.
Proper ventilation also significantly improves energy efficiency in your home. Keeping the attic cooler in summer reduces the workload on your air conditioning system, potentially lowering cooling costs. In winter, it helps maintain a dry attic, improving the effectiveness of your insulation and potentially reducing heating costs.
In colder climates, good ventilation helps prevent ice dams, which can cause serious water damage to your roof and home interior. Additionally, by controlling moisture levels, proper ventilation reduces the risk of mold and mildew growth, contributing to a healthier indoor environment and preserving the structural integrity of your home.
Signs of Poor Ventilation
Excessive heat in the attic is one of the clearest signs of poor ventilation. If your attic feels significantly warmer than the outside temperature on a hot day, it may indicate insufficient airflow. This can lead to increased cooling costs and potential damage to roofing materials.
Moisture issues are another key indicator of ventilation problems. Signs can include dampness or frost in the attic during winter, water stains on the ceiling, or visible mold growth. These issues not only signal poor ventilation but can also lead to serious structural damage if left unaddressed.
External signs of ventilation issues may also be visible. Curling shingles or paint peeling on the underside of roof overhangs often indicate excessive heat and moisture in the attic. Additionally, if you notice your heating and cooling costs rising inexplicably or if your home feels constantly stuffy, these could be signs that your roof ventilation needs special attention.

Conclusion
We hope this article has helped you understand better the crucial role roof vents play in maintaining a healthy home. So, what are roof vents for? As this guide has revealed, the answer encompasses a wide range of benefits but mainly serves to regulate the temperature and moisture in homes. More than that, it improves energy efficiency and extends your roof’s lifespan. By understanding the various types of vents and their functions, you’re now better equipped to ensure your home’s ventilation system works effectively.
Remember, a well-ventilated roof is key to a comfortable, energy-efficient, and structurally sound home. If you’ve noticed any signs of poor ventilation, don’t hesitate to consult a professional. Investing in proper roof ventilation today can save you from costly repairs and discomfort in the future.