When designing or renovating a home, the choice between a hip roof and a gable roof is a decision that carries significant weight. These two popular roofing styles significantly impact not only the aesthetics of a house but also its functionality, durability, and cost.
Hip roofs, with their sloping sides, and gable roofs, characterized by their triangular shape, each offer distinct advantages and challenges. That’s why selecting between hip vs gable roof involves evaluating various factors such as climate, architectural style, building codes, and personal preferences.
The choice between hip and gable roofs extends beyond visual appeal; it also encompasses practical considerations such as attic space, ventilation systems, and even insurance premiums. It may also affect the ease of future expansions or the installation of solar panels.
In the following, we will delve into the key differences between hip and gable roofs, examining their structural characteristics, weather resistance, energy efficiency, and overall impact on home design.
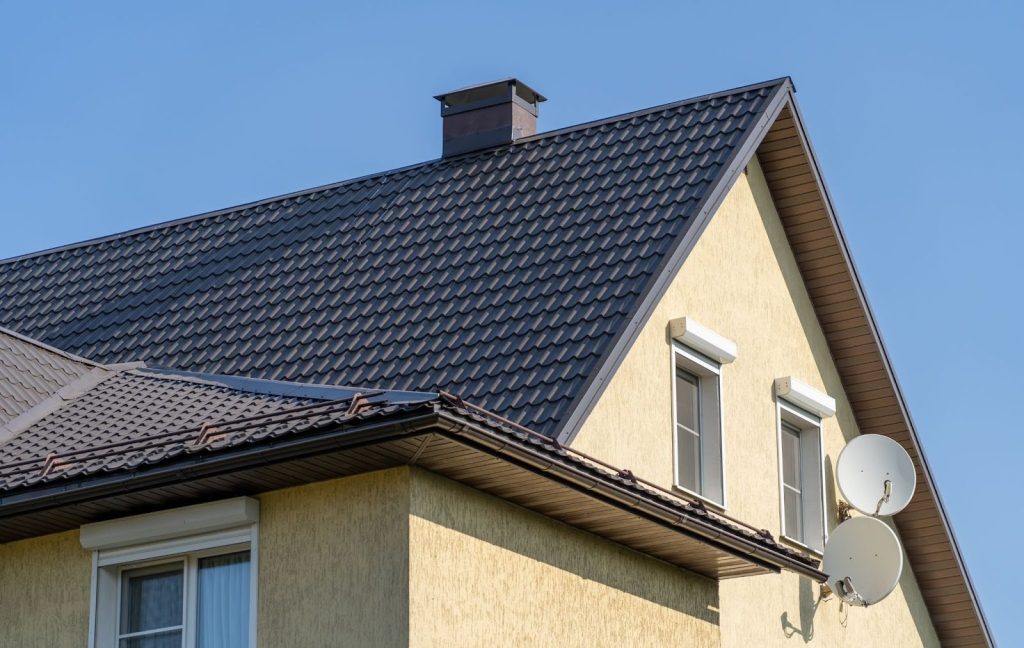

Hip vs Gable Roof
A hip roof features slopes on all four sides that come together at the top to form a ridge, creating a compact, sturdy structure with no vertical ends. This design offers excellent wind resistance and allows for consistent eaves around the entire house. It provides good protection for walls and creates opportunities for extra living space or storage in the attic.
In contrast, a gable roof has two sloping sides that meet at a central ridge, forming a triangular shape at each end known as a gable. This classic design allows for more attic space and better water drainage, making it popular in areas with heavy rainfall or snow. Gable roofs are often simpler to construct and can be more cost-effective, but may require additional bracing in high-wind areas.
What is a hip roof?
A hip roof is characterized by slopes on all four sides of the structure. These slopes meet at the top to form a ridge, creating a distinctive pyramid-like shape. This design provides greater stability compared to other roof types. The inward slope of all sides makes hip roofs particularly resistant to strong winds, making them a popular choice in hurricane-prone areas.
Hip roofs also offer excellent drainage for rain and snow, reducing the risk of water damage.
What is a gable roof?
A gable roof is defined by its two sloping sides that meet at a central ridge, forming a triangular shape at each end of the building. This classic design is known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it one of the most common roof types in residential architecture.
Gable roofs are relatively easy to construct, which often translates to lower building costs. They provide excellent water drainage and create ample attic space, which can be used for storage or converted into living areas.
The steep pitch of many gable roofs makes them well-suited for regions with heavy snowfall, as the snow easily slides off the sides. This design also allows for good ventilation, helping to regulate temperature and moisture in the attic space.
Pros and cons of hip roofs
Pros
- Better wind resistance due to sloped design on all sides
- Enhanced durability and stability
- Longer lifespan compared to other roof types
- Improved energy efficiency with consistent eaves for shade
Cons
- More expensive to construct due to the complex design
- Requires additional materials, increasing costs
- More challenging to build, potentially increasing labor costs and construction time
- Limited attic space for storage or living area
Pros and cons of gable roofs
Pros
- Provide excellent ventilation
- Easier to construct
- More affordable due to simpler design
- Offer ample attic space for storage or living area
Cons
- Less stable in high winds
- More prone to damage in hurricane-prone areas
- Can experience uplift in severe weather conditions
- May require additional bracing in some regions
Hip Roof vs Gable Roof Cost
Hip roofs generally cost more to construct than gable roofs due to their complex design and additional materials required. The intricate structure of a hip roof, with slopes on all four sides, necessitates more roofing materials and labor, increasing overall expenses.
Gable roofs, with their simpler two-slope design, are typically less expensive to build. Their straightforward construction requires fewer materials and less labor time, making them a more budget-friendly option for many homeowners.
However, long-term costs should also be considered. Hip roofs often provide better durability and wind resistance. This can potentially lead to lower maintenance and repair costs over time compared to gable roofs in certain climates.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between the hip vs gable roof depends on various factors specific to each homeowner’s needs. Hip roofs offer superior wind resistance and durability, making them ideal for hurricane-prone areas. However, they come with higher initial costs and more complex construction. Gable roofs, on the other hand, provide simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and excellent ventilation but may be less stable in high winds.
Consider your local climate, budget, and architectural preferences when making your decision. Factor in long-term costs, including potential maintenance and repairs. Consult with local builders or architects who understand regional weather patterns and building codes.
Ultimately, both hip and gable roofs have stood the test of time, each offering unique advantages. The best choice is the one that aligns with your specific requirements and circumstances.